Work Energy Theorem
Work Energy Theorem: Overview
This topic covers the concept of Work Energy Theorem.
Important Questions on Work Energy Theorem
A satellite of mass , initially at rest on the earth, is launched into a circular orbit at a height equal to the radius of the earth. The minimum energy required is
A object has initial velocity The total work done on the object if its velocity changes to is
A variable force acts on body of mass and it changes the velocity of the body from to . Find the work done (in ) on the body by the variable force.
Work energy theorem is applicable for conservative forces only.
A body of mass travels in a straight line with velocity . What is the work done by the net force during its displacement from to ?
Three identical solid spheres move down through three inclined planes all same dimensions, is without friction, is undergoing pure rolling and is rolling with slipping. Compare the kinetic energies at the bottom.
A body of mass thrown vertically upward from the ground with a velocity of reaches a maximum height of . Magnitude of work done by the air resistance is (Acceleration due to gravity )
A car of mass is moving at a speed of up an inclined plane making an angle with the horizontal. At some point, the motor stops, and the car continues to move along the plane due to its initial velocity. If it is just able to reach the destination which is at a height of above the point, calculate the work done against friction acting between the tyres of the car and the plane. (Assume )
An object of mass moves along positive axis. When it passes through a constant force directed along the negative axis begins to act on it. The kinetic energy of the object is found to be and for and respectively. If the force continues to act further, then the object moves back along negative axis. The speed of the object when it reaches
What minimum horizontal velocity has to be imparted the ball suspended from a thread of length for it to reach the height of the suspension?
What is the critical speed of block of mass tied to one end of a string which is whirled round in a vertical circle of a radius at the top of the circle?
An electron and a proton are moving under the influence of mutual forces. In calculating the change in the kinetic energy of the system during motion, one ignores the magnetic force of one on another. This is because
A body of mass is put under a forces which in turn causes a displacement in it is given by What will be the work done by the force in first ?
A particle of mass lying on-axis experiences a force given by law, . Where, is the coordinate of the particle in .
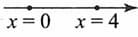
A two-dimensional force field acts on a particle where force is in newton and is in meter. The particle moves from the coordinates to . Calculate the kinetic energy change during this process. (The coordinates are in meter.)
The system have initial configuration as given in the figure
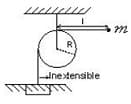
Now, The bob is released and the string starts wrapping around the pulley. (The pulley is held in place by a force applied at the centre.Given that, string and the pulley are light.)
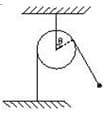
What is the tension in the string as a function of ?
If a solid cylinder of mass is rolling on a horizontal surface with a velocity of . It collides with a horizontal spring of spring constant . What will be the maximum compression produced in the spring?
A wooden block of mass is pushed on a movable wedge of mass and height with a velocity . Before striking the wedge it travels on a rough horizontal portion. Velocity of the block is just sufficient to reach the top of the wedge. Assuming all surfaces are smooth except the given horizontal part and collision of block and wedge is jerk less, the friction coefficient of the rough is(Take )
 .
.
A curved surface is shown in figure. The portion is free of friction. There are three spherical balls of identical radii and masses. Balls are released from rest one by one from which is at a slightly greater height than .

With the surface , ball has large enough friction to cause rolling down without slipping. Ball has a small friction and ball has a negligible friction.
For balls which do not reach , which of the balls can reach back ?
